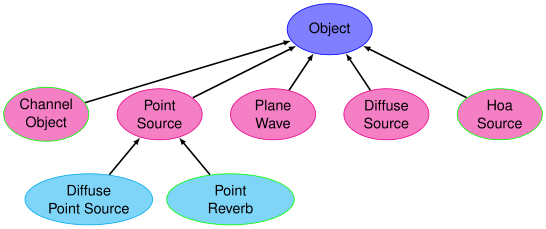
The VISR object model¶
The VISR object model supports a hierarchical and extensible set of object types. These types and their relations are shown above.
JSON representation¶
For transmission, object vectors are encoded as JSON messages.
A scene vector (or a part thereof) has the format
"objects": [ {<object 0>}, {<object 1>}, ... , {<object n>}]
where <object k> stands for the encoding of a single object. The objects can be arranged in arbitary order as long as the object ids are unique. Moreover, the object vector can be split into arbitrary subsets and be transmitted as individual "objects" messages.
Encoding of the individual object types¶
Coordinate system¶
Depending on the object type, either Cartesian and spherical coordinates are use. The coordinate axes follow, e.g., the ITU-R BS.2051 conventions.
For Cartesian coordinates, this means:
- x axis points to the front
- y axis points to the left.
- z axis points up.
Coordinates are measured in meters.
Likewise, for spherical coordinates:
- The azimuth angle is measured counterclockwise from the x axis (front).
- The elevation angle is measure up (positive values) or down (negative values) from the horizontal plane.
Coordinates are represented in the JSON format in degree (this does not necessarily hold for the internal representation in the renderer).
Object¶
Object is the base type of all objects. Therefore, the attributes are common to all objects.
The following attributes are supported:
"id"- The object id, a nonnegative integer that must be unique withing the object vector (mandatory attribute).
"group"- The group id, a nonnegative integer (mandatory attribute). Not used in the core renderer, but potentially in the metadata adaptation process.
"channels"- A list of audio channel indices referencing the audio signals associated with this object. The list is formed as a string consisting of comma-separated unsigned integers enclosed in quotation marks, e.g., “0,3, 5, 7 ” with arbitrary amounts of whitespace in between. The format also allows Matlab-style ranges for any part of the list. For instance, “0, 2 : 2 : 8, 10” is equivalent to “0,2,4,6,8,10”. This is a mandatory argument. The reuired number of channels is typically determined by the object type and its parameters. For instance, point source objects are invariably single-channel, while the number of required channels of a HOA object depends on the Ambisonics order specified by the “order” of this object.
"level"- The level of the audio object in linear scale as a floating-point number. Note that this value does not necessarily denote the loudness of the reproduced object, since the latter also depends on the level of the audio signal(s). (Mandatory argument).
"priority"- The priority of the object given as an unsigned integer (mandatory argument). Lower numbers represent higher priority, with “0” being the highest prority. Not currently used in the core renderer, but potentially (and moe appropriately) in the metadata processing.
"eq"- An array of parametric EQ parameters to be applied to all audio signals for this object. This is an optional attribute, if not present, a ‘flat’, i.e., unity-gain equalisation curve is applied. The attribute has the format
"eq": [{<eq 0>}, {<eq 1},...{<eq n-1>}]
: The number of admissible EQ sections is renderer-dependent. Providing more EQ parameters for a single object than supported by the renderer might result in an error message and termination of the renderer. If less EQ parameters are sent than supported by the renderer, the remaining EQ sections are padded with ‘flat’ characteristics. The individual EQ section have the form
{ "type": "<type>", "f": (center/cutoff frequency), "q": (quality) [, "gain": (dB) }
with the following attributes:
"type"- A type string chosen from the following values:
"lowpass","highpass","bandpass","bandstop","peak","lowshelf","highshelf","allpass". "f"- Centre/cutoff frequency in Hz (depending on the filter type).
"q"- Dimensionless Q (quality) parameter.
"gain"- Optional gain parameter (in dB). If not provided, the default value of 0 dB is used. Only used by the filter types
"peak","lowshelf", and"highshelf". The filter characteristics follow the Audio EQ Cookbook formulas.
PointSource¶
Point sources are invariable single-channel objects, that is the "channels" attribute of the base type Object must contain a single channel index.
The type string is "point".
The point source coordinates sre specified in the "position", which is an object holding either Cartesian coordinates "x", "y", and "z" or spherical coordinates "az", "el", "radius"
Example¶
{ "id": "5", "channels": "2", "type": "point", "group": "2", "priority": "0", "level": "0.350",
"position": {"x": "3.0", "y": "-0.5", "z": "0.25" } }
or, using polar coordinates,
{ "id": "5", "channels": "2", "type": "point", "group": "2", "priority": "0", "level": "0.350",
"position": {"az": "30", "el": "15.0", "radius": "1.25" } }
PlaneWave¶
Plane waves differ from point sources that they do not exhibit distance-dependent attenuation and do not provide parallalax effects for moving listener positions. Because the main reproduction method in the VISR renderer at the moment is VBAP, plane waves are handled identically to point sources. This might change for alternative reproduction methods, including listener position adaptive VBAP.
Plane waves use the type "plane" and are single-channel objects.
The plane wave representation uses an object "direction" containing the attributes "az" and "el" to describe azimuth and elevation of the direction of the impinging source. The third parameter "refDist" (reference distance) encodes the relative timing of the object’s audio signal: A value of 0 means that a sound event at signal time 0 is perceived at the central listener at time 0.
Example¶
{"id": 5, "channels": 5, "type": "plane", "group": 0, "priority": 0, "level": 1.000000, "direction": {"az": 30.0, "el": 45.0, "refdist": 12.00 } }
PointSourceDiffuse¶
Point source with diffuseness are derived from PointSource and therefore support all attributes of the latter.
In addition they define the attribute "diffuseness" that is a floating-point supposed to be in the range between 0.0 and 1.0 and describes the amount of diffuse energy relative to the point source radiation.
They are single-channel and use the type string "pointdiffuse".
Example¶
{"id": "5", "channels": "5", "type": "pointdiffuse", "group": "0", "priority": "0",
"level": "1.0", "diffuseness": "0.35", "position": {"x": "3.0", "y": "-0.5", "z": "0.25" } }
DiffuseSource¶
This source type describes a surrounding objects reproducing decorrelated signals obtained from the single object audio signal.
This object does not introduce any other attributes apart from those inherited from the base class Object. The type string is "diffuse".
Example¶
{"id": 3, "channels": 3, "type": "diffuse", "group": 0, "priority": 0, "level": 1.000000}
HoaSource¶
This source type represents a Ambisonics sound field of arbitrary order. It is a multichannel object where the number of channels depends on the Ambisonics order \(N\): \(ch=(N+1)^{2}\). The audio signals (as indexed by the "channels" attribute, are expected to be in ACN channel order http://ambisonics.ch/standards/channels/.
The type string is "hoa".
Example¶
{"type": "hoa", "channels": "0:8", "group": 0, "id": 0, "level": 1, "order": 2, "priority": 0},
ChannelObject¶
Channel objects are audio signals that are routed directly to a loudspeaker (or group of loudspeakers) specified by an id.
This type is derived from Object and adds the "outputChannels" attribute. This attribute is a string contains a list of loudspeaker ids (i.e., labels).
Channel objects can contain an arbitrary number of channels. The outputChannels must contain an entry for each channel. This can be either a single label or a list of labels enclosed in square brackets.
In the latter case, the respective channel is routed to the list of loudspeakers.
An diffuseness attribute controls the level of decorrelation applied, from 0.0 (no decorrelation) to 1.0 (fully replayed to the decorrelation filters). OPtional attribute, default is 0.0.
If a channel is routed to more than one loudspeaker, the levels of these loudspeakers are normalised using the same norm as the respective panner (VBAP, VBIP in case of separate high-frequency panning, or diffuse panning).
Example¶
Single-channel object routed to a single loudspeaker:
{"id": 2, "channels": "3", "type": "channel", "group": 0, "priority": 0, "level": 0.50000, "diffuseness": 0.5,
"outputChannels": "M+030"} ]
Alternative syntax for single-channel syntax :
{"id": 2, "channels": "3", "type": "channel", "group": 0, "priority": 0, "level": 0.50000, "diffuseness": 0.5,
"outputChannels": "[M+030]"} ]
Single channel routed to multiple loudspeakers:
{"id": 2, "channels": "3", "type": "channel", "group": 0, "priority": 0, "level": 0.50000, "diffuseness": 0.5,
"outputChannels": "[M+030, M-030]"} ]
Multiple channels routed to single or multiple loudspeakers:
{ "id": 2, "channels": "4:8", "type": "channel", "group": 0, "priority": 0,
"level": 0.350000, "diffuseness": 0.25,
"outputChannels": "M+000, [M+030], [M-030, U+030], U+110"}]
PointSourceWithReverb¶
PointSourceWithReverb is a single-channel object that adds reverb to a PointSource. It uses the type string "pointreverb".
In addition to the Object and PointSource properties it defines an attribute “room” containing the objects "ereflect" (early reflections) and "lreverb" (late reverberation). "ereflect" is an array of early reflection objects, consisting of IIR coefficients ("biquadsos", a point source position "position" using the same format as in PointSource, and additional level and delay information.
The maximum number of discrete reflections per reverb object is a configuration parameter of the renderer.
The "lreverb" object contains parameter data in fixed frequency bands that are used to synthesize reverb tails.
Example¶
{ "type": "pointreverb", "channels": "4", "group": 0, "id": 1,"level": 1,
"position": {"x": 1.5, "y": 0.0, "z": 0.0}, "priority": 0,
"room": {
"ereflect": [{"biquadsos": [{"a0": "1.00000e+00", "a1": "-1.05734e+00", "a2": "5.69314e-01",
"b0": "3.87648e-01", "b1": "0.00000e+00", "b2": "0.00000e+00"},
( more biquad coefficients)
{"a0": "1.00000e+00", "a1": "-7.20132e-02", "a2": "6.48827e-01",
"b0": "1.00000e+00", "b1": "0.00000e+00", "b2": "0.00000e+00"}],
"delay": "0.00931", "level": "0.0603584806", "position": {"az": 337.0, "el": "-1.00000", "refdist": "1.00000"} },
( more early reflections )
],
"lreverb": {"attacktime": "0.01321, 0.01321, 0.01321, 0.01321, 0.01321, 0.01321, 0.01321, 0.01321, 0.01321",
"decayconst": "-4.50698, -5.02028, -5.75817, -5.36509, -5.42654, -5.62316, -5.75298, -6.41075, -11.13465",
"level": "0.02522, 0.01052, 0.01657, 0.02744, 0.02058, 0.01679, 0.01698, 0.01433, 0.00041", "delay": "0.00931" } }